NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
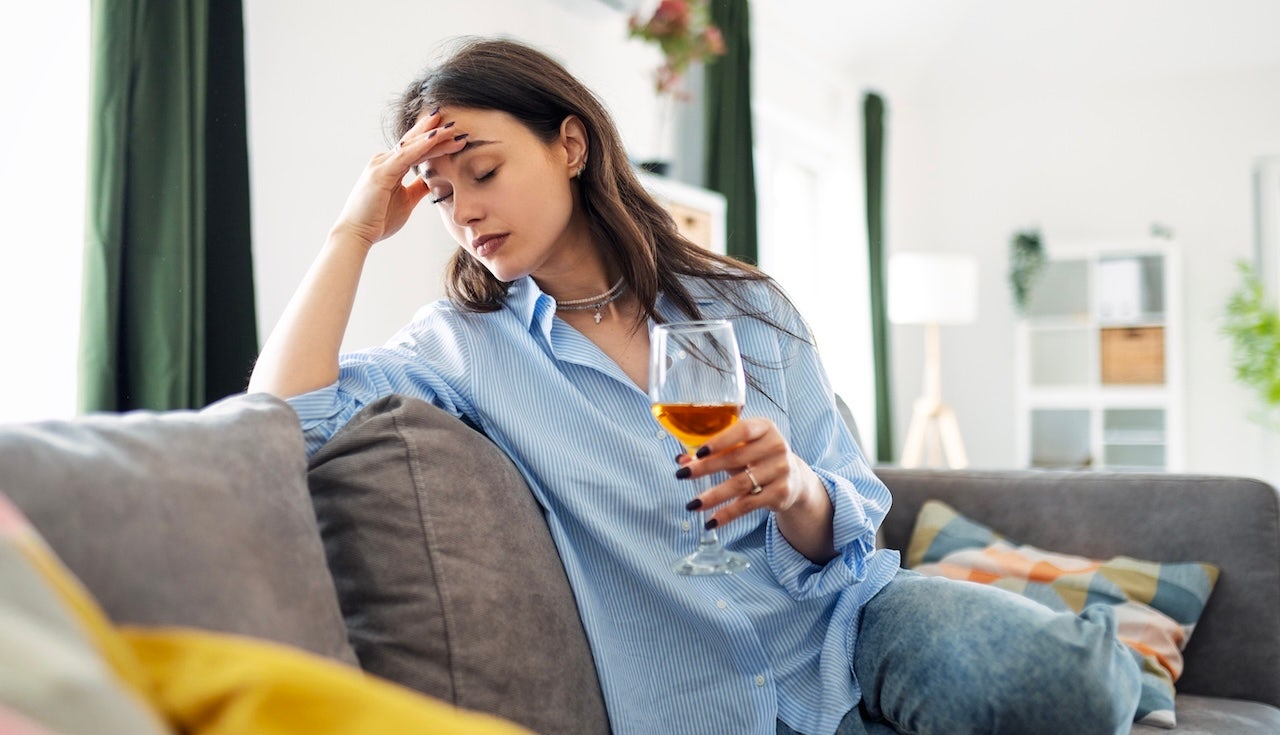
Recent studies continue to support a decades-old drug as an alternative means of reducing alcohol consumption.
The prescription opioid pill, called naltrexone, was first approved by the FDA to treat opioid dependence in 1984. A decade later, it was approved for alcohol use disorder.
In addition to the daily pill version, naltrexone is also available as a monthly injectable therapy, which was approved for alcohol use disorder in 2006 and opioid use disorder in 2010.
POPULAR WEIGHT-LOSS DRUGS COULD TAKE THE EDGE OFF YOUR ALCOHOL BUZZ, STUDY FINDS
How it works
Naltrexone works by blocking opioid receptors in the brain. For those dependent on opioids, it blocks the “euphoric” effects of the drugs and also curbs cravings for alcohol, according to experts.
“Naltrexone can be used to assist with reducing alcohol cravings and reduce the pleasurable effects from alcohol ingestion, which can help those prone to binge-drinking to consume less volume,” Dr. David Campbell, clinical director and program director at Recover Together, a behavioral health and addiction treatment facility in Bend, Oregon, told Fox News Digital.
HIGHER STROKE RISK LINKED TO CONSUMING CERTAIN AMOUNT OF ALCOHOL, STUDY FINDS
The medication is useful for people who experience strong cravings, often drink to excess once they start, or drink primarily due to reward or relief as opposed to habit, according to Campbell.
“Naltrexone affects the rewards center of the brain, which blocks the rewarding effects of alcohol.”
Jessica Steinman, chief clinical officer at No Matter What Recovery in Los Angeles, calls naltrexone “an incredibly helpful and life-saving tool” for people who struggle with alcohol use disorder.
“Currently, in our society, many people are looking to get medication-assisted help from overconsumption of certain things or behaviors, including food, cigarettes and now alcohol,” she told Fox News Digital.
FIRST-OF-ITS-KIND FENTANYL VACCINE TARGETS OVERDOSES BEFORE THEY START
“Naltrexone affects the rewards center of the brain, which blocks the rewarding effects of alcohol and cravings to be minimized. It can assist in telling the brain that alcohol isn’t wanted.”
The drug can also help if someone has a “healthy” relationship with alcohol and is looking to cut back on their drinking behaviors, Steinman added.
“We do not suggest moderation in any way for people struggling with alcohol use disorder or any type of dependence to alcohol or other substances,” she noted. “We do not believe drinking ‘less’ is a solution.”
Side effects
Common side effects of naltrexone can include nausea and vomiting, headache, sleep disturbances, dizziness, fatigue, anxiety, loss of appetite, and joint or muscle pain, according to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
These effects are generally mild and may improve as the body adjusts to the medication.

In rare cases, patients may experience more severe effects, such as liver issues, allergic reactions, trouble breathing and mental health effects.
“The most important thing when taking naltrexone for alcohol use is to ensure that there is no concurrent use of opioids, as taking naltrexone when using opioids can induce precipitated withdrawal, a very uncomfortable event,” Campbell cautioned.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
More than 50% of U.S. adults drink alcohol, about 17% are classified as binge-drinkers and about 6% drink heavily, according to CDC data.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE HEALTH STORIES
Each year, around 178,000 deaths in the country are linked to excessive alcohol use.
“Heavy alcohol consumption and binge-drinking can lead to many health problems and make chronic health conditions worse, so reducing alcohol intake can really improve health,” Donita Robinson, Ph.D., an associate professor of psychiatry at the UNC School of Medicine in North Carolina, told Fox News Digital.
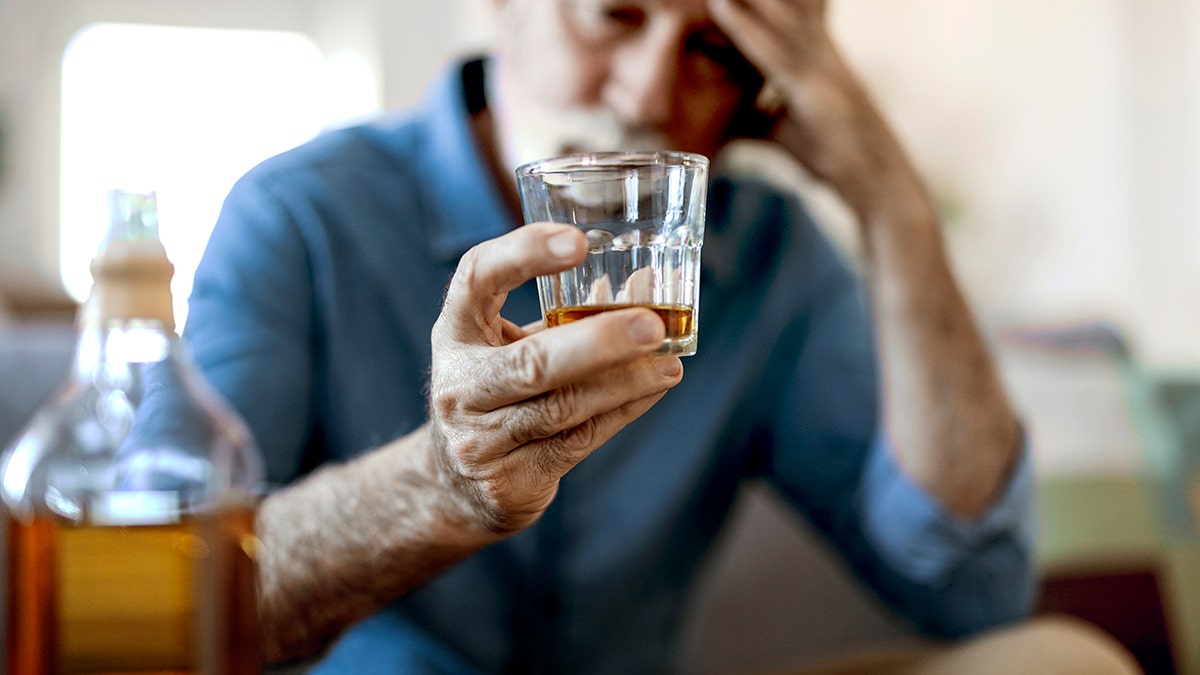

“Naltrexone helps many people reduce their drinking – it’s an effective medication to reduce alcohol craving and heavy drinking, and it works best in combination with counseling or other therapy.”
Robinson reiterated that people who are on opioid medications, including some painkillers, shouldn’t take naltrexone, as it can block their effectiveness and cause opioid withdrawal.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FOX NEWS APP
Naltrexone is available with a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider, such as a primary care doctor, addiction medicine specialist or psychiatrist.
Health officials warn against purchasing the drug online or without a prescription, as it may be counterfeit and unsafe.
TEST YOURSELF WITH OUR LATEST LIFESTYLE QUIZ
Those interested in exploring whether naltrexone is an option for them should see a doctor, who can assess the safety of the drug based on the patient’s medical status and history.
They should also “make sure they have their goals and intentions in line before using a medication like this,” according to Steinman.
Read the full article here